код ошибки 0x534 sqlstate 42000 ошибка 15404
MSSQLSERVER_15404
Сведения
| attribute | Значение |
|---|---|
| Название продукта | SQL Server |
| Идентификатор события | 15404 |
| Источник события | MSSQLSERVER |
| Компонент | SQLEngine |
| Символическое имя | SEC_NTGRP_ERROR |
| Текст сообщения | Не удалось получить сведения о пользователе/группе Windows NT «пользователь«, код ошибки код_ошибки. |
Объяснение
15404 используется при проверке подлинности, если указан недопустимый участник. Или олицетворение учетной записи Windows не выполняется, так как не существует связи полного уровня доверия между учетной записью SQL Server и учетной записью домена Windows.
Действие пользователя
Убедитесь, что участник Windows существует и его имя указано верно.
Если эта ошибка — результат отсутствия связи полного уровня доверия между учетной записью службы SQL Server и учетной записью домена Windows, то ошибку можно устранить одним из следующих способов.
Используйте для службы SQL Server учетную запись из домена, к которому относится пользователь Windows.
Если SQL Server использует учетную запись компьютера, например Network Service или Local System, то домен, на котором находится пользователь Windows, должен доверенную связь с компьютером.
Fixing Maintenance Plan Error code 0x534
Have you ever changed Server name on which SQL Server instance is installed? One of my friends changed the hostname of a Windows server with SQL Server already installed. After this, the SQL Server maintenance plan jobs started to fail. As we know, internally SQL Server still shows the old hostname this must be dropped manually. Otherwise your SQL Server maintenance plan jobs fail with this error.
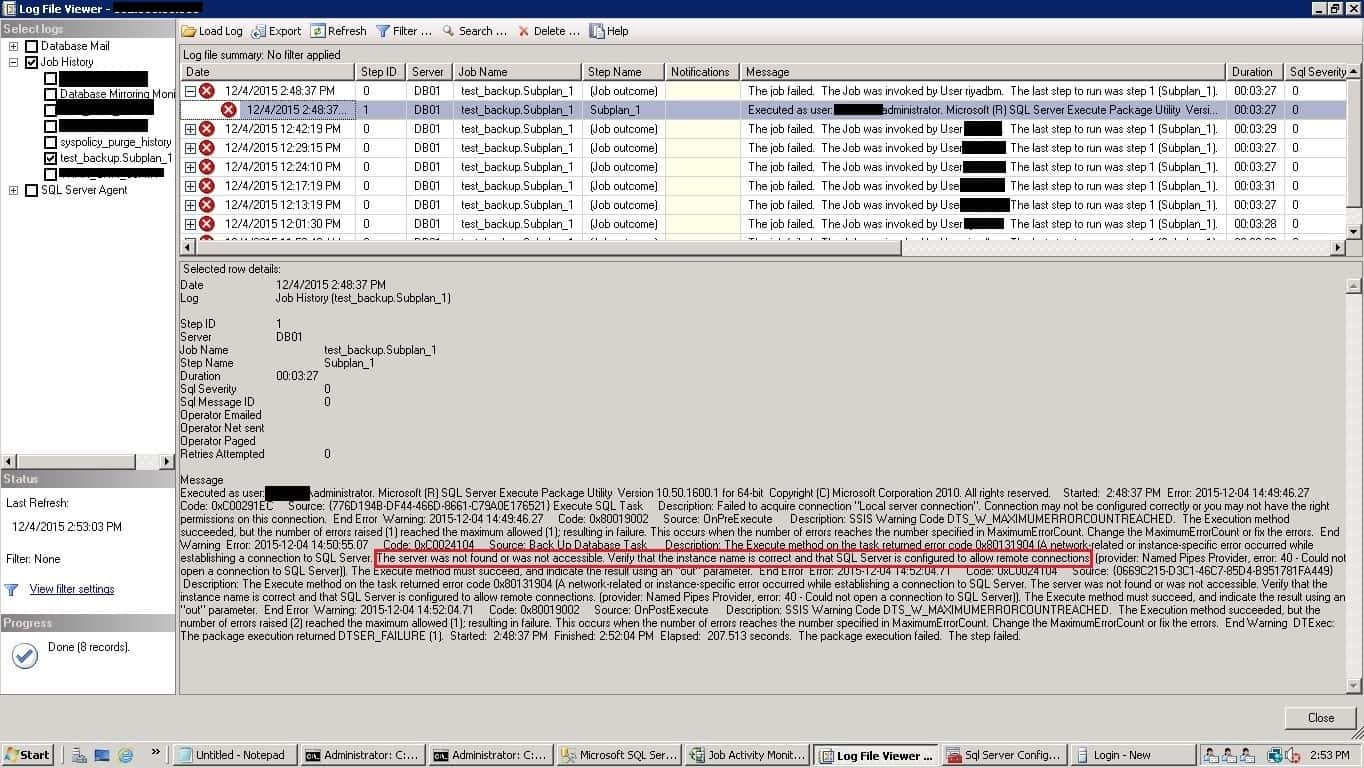
The Job failed: Could not obtain information about Windows NT group/user ‘XXXXXX\Administrator’, error code 0x534. [SQLSTATE 42000] (Error 15404))
In this post, I will show you the procedure to resolve the errors and execute the SQL Server Agent Maintenance Plan jobs successfully. Below is the error screenshot showing job failure in the SQL Server agent logs. The error is highlighted in the image in red.
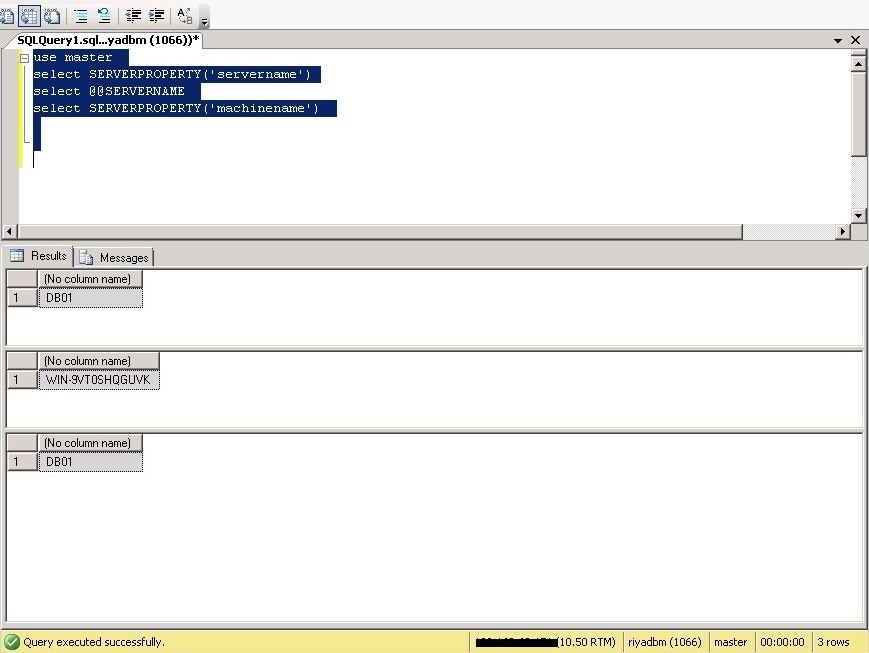
First, connect to your SQL Server instance with SQL Server Management Studio and run the below queries to check SQL Server name:
In the below screenshot, the server name and machine name are different.
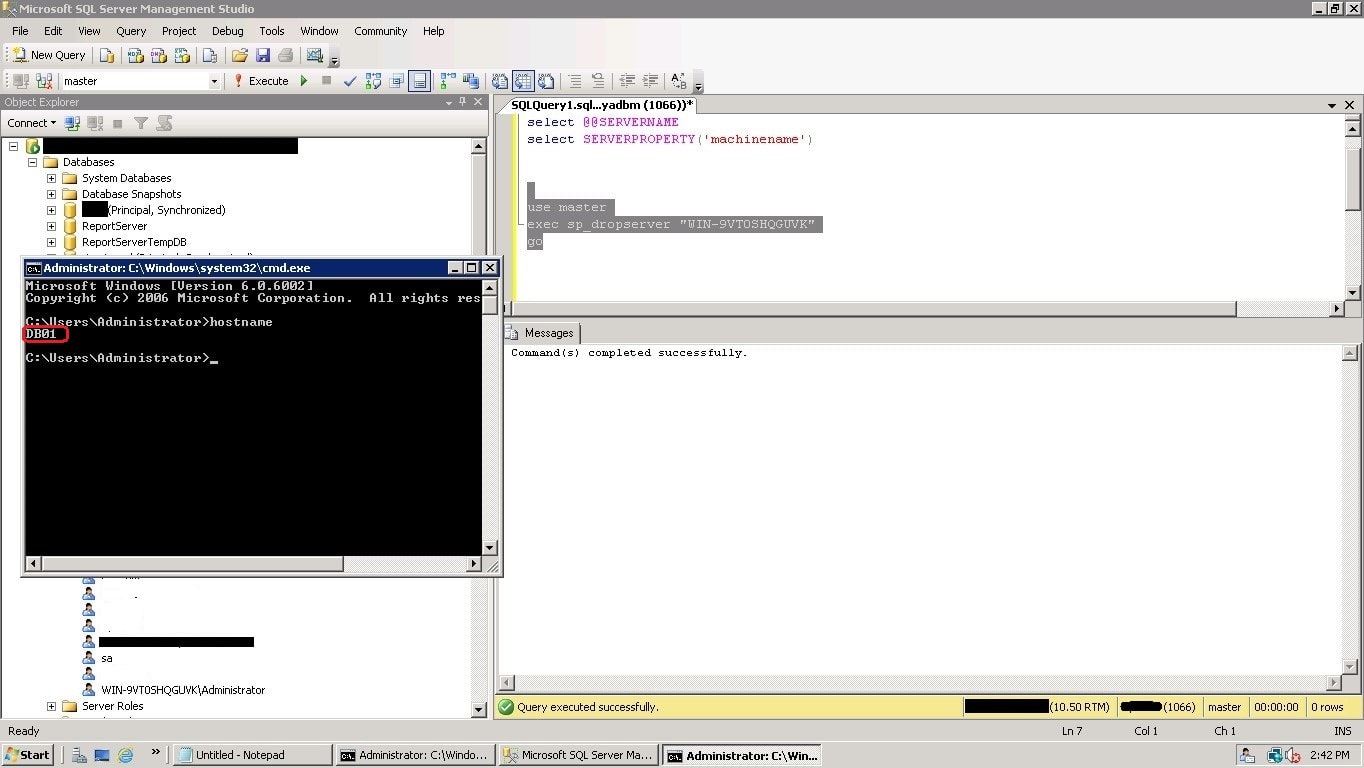
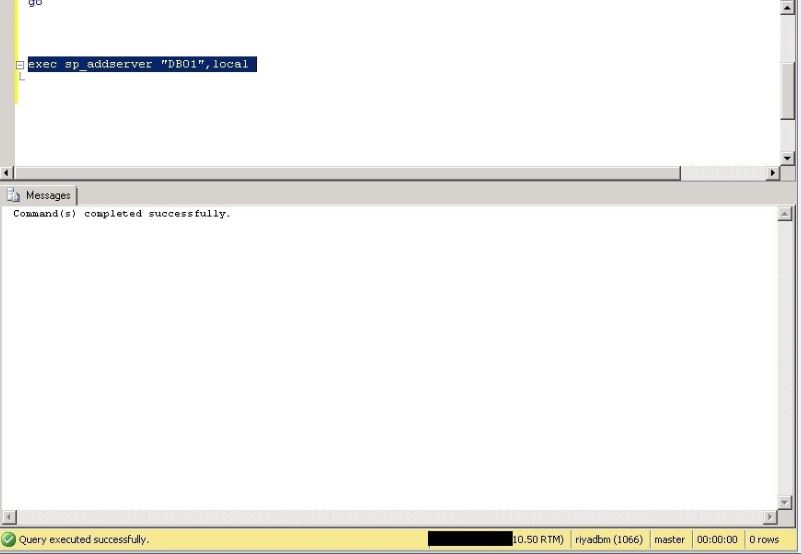
Run the below shown T-SQL scripts to drop the old server name, and then it add back the SERVERNAME to match the operating system’s hostname.
In the below screenshot, first we dropped old server name.
In the below screenshot, we have added new server name using T-SQL.
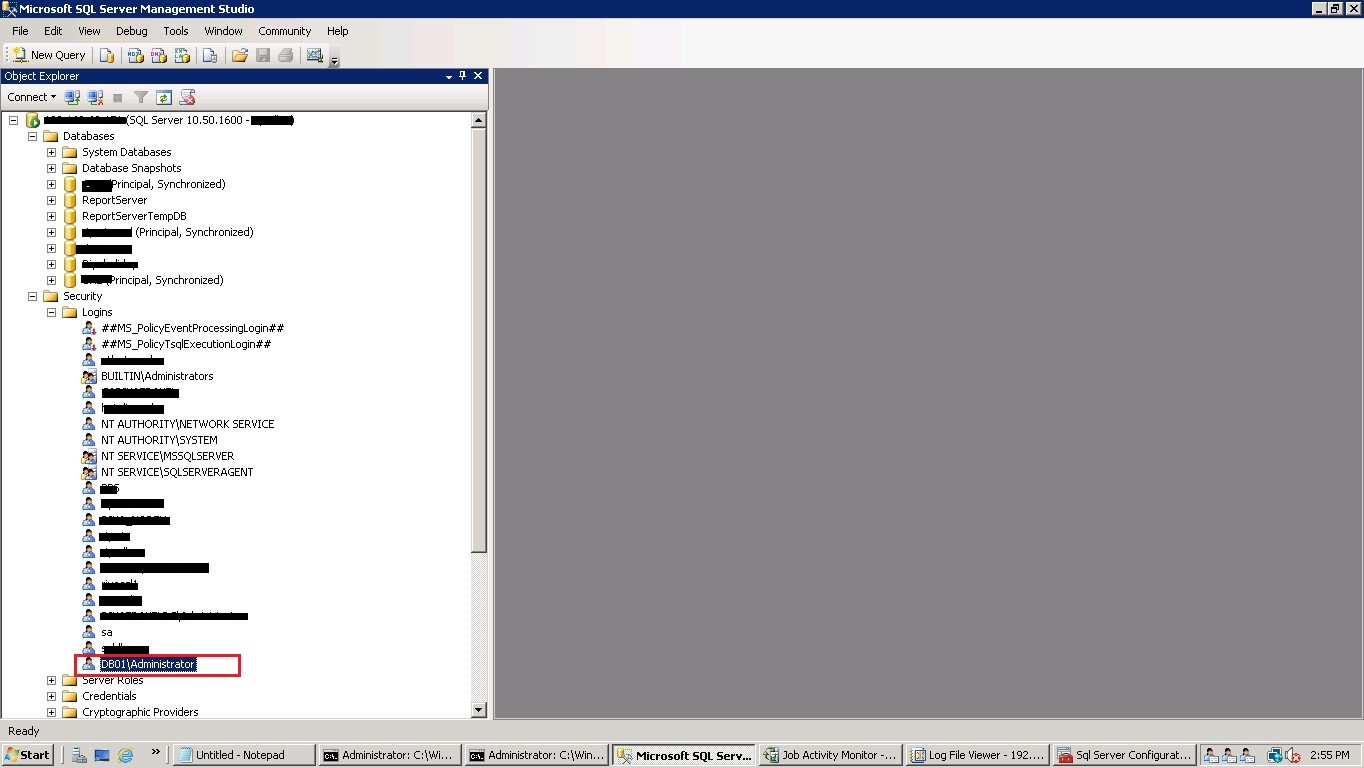
Now, log into the SQL Server with a “sysadmin” privileged user. Go to SQL Server logins, and you can still see the oldServername\administrator login bound with the SQL Server engine.
Drop the login “OldServername\administrator” and create a new windows login as “NewServername\administrator”, adding the sysadmin Server role.
In the below screenshot, we have added “DB01\administrator” login.
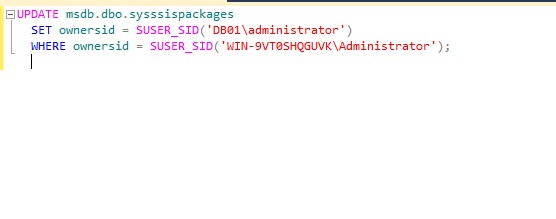
The owner of the job associated with maintenance plan is OldServername\administrator. We need to reset the ownerid using the below T-SQL Update query.
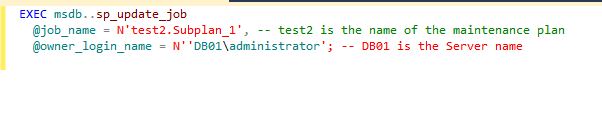
Now, We need to reset the owner of the job associated with the maintenance plan by running the below T-SQL query. In below screenshot, reset the owner of the job.
Right click on SQL Server job and select properties and change the owner of job to “sa” login.
Delete old maintenance plan and re-create the maintenance plan. Right click and click execute maintenance plan. You can see maintenance plan executed successfully. J
Код ошибки 0x534 sqlstate 42000 ошибка 15404
I executed the following:
EXECUTE AS LOGIN=’ADS\me’
Go
Msg 15404, Level 16, State 19, Line 1
Could not obtain information about Windows NT group/user ‘ADS\me’, error code 0x5.
I also executed that command with the service account:
EXECUTE AS LOGIN=’ADS\myserviceaccountname’
Command(s) completed successfully.
So, it’s as if the service account can query its own information but not that of other ads user objects. I suspect that SQL is trying to validate my SID with the SID it has for me within a SQL system table to verify that my ADS account really is a SQL login, but I’m just guessing there.
I’m going to send this information to our ADS admins. It really seems to point to a permission problem in ADS.
If it is a SQL issue, could it be that ADS\me doesn’t have permission to execute a system stored procedure in order to perform the ADS query? To answer my own question, it seems like the service account would be doing this and not my ADS\me account.
I have to admit I am also a little bit surprised. I have never faced a scenario where an account is getting an explicit access denied when querying information about itself and all its groups, but succeeds while querying information about other principals and objects in the AD. I agree with you, check with your AD administrator, probably they have some security policy we are not aware of that may be causing this problem.
I personally don’t think the problem is regarding any permission to execute a system stored proc (EXECUTE AS should call the code directly); but let’s wait until we have more information from the AD admins regarding this issue.
One more thing you can try: Can you install a test-only copy of SQL Server 2005 (i.e. SQL Server Express) using a different account for the service? (it could be a different machine). If you can install it, can you try the same EXECUTE AS LOGIN tests?
Actually, I think it’s the other way around: the service account can query its own information, but cannot query other ADS users.
I’ll see if I can try that test on my local SQL instance.
Got it, I misunderstood that part; I apologize for the confusion. Thanks for the clarification.
It seems like it is a limited account on the AD and doesn’t have permission to query, hopefully the AD admin will be able to verify if this assumption is correct.
I am having the same exact problem. I even test on my test SQL server and I get the same message. I am not sure where to start to solve this problem. Any help?
Make sure that the SQL Server service account has permission to query the AD. Typically this error is caused by trying to impersonate or query information regarding a Windows user from a different domain.
Please, if you need further assistance let us know the scenario that were you are hitting this issue.
Can you give me the step by step on how to grant, or make sure, the SQL Server service account has access to query AD? I’m new to SQL and not sure how to do this. I have two domains setup. One is internet facing, and one is our regular domain. Our regular domain doesn’t trust out Interent domain, but our Internet domain trusts our regular domain. The SQL server I am working on is in our Internet domain, and the jobs are falling with the same messages above. We are running a few jobs with different user accounts. Some from our regular domain, and a few with our admin account on the Internet domain. All jobs are falling. I have tried running the jobs with the sa account, but that fails as well.
Can you help me out?
Hello,
I am also getting the same error (15404) as Syndrake. I have tried all of Raul’s suggestions with the same results.
I have confirmed with our AD Admin that there are no restrictions on this domain account. They setup the service account as a standard user. She actually created a new account, just as a test, while I had her on the phone and we had the same results.
One intresting twist with my situation is that this issue cropped up when I migrated this server to an AD domain from a NT4 domain (seperate domains, not a domain upgrade). The Agent service account was able to query user info just fine in NT 4, but this same SQL Agentservice/job owner setup now fails in AD.
For further assistance on AD configuration I would recommend using the directory services forum ( http://forums.microsoft.com/TechNet/ShowForum.aspx?ForumID=571&SiteID=17 ), the audience of this forum will be better qualified to help you on this area than myself.
Please correct me if my assumption is incorrect:
· Domain-A trusts Domain-B, but Domain-B doesn’t trust Domain-A
· SQL Server is installed on a Domain-A machine
In order to work, SQL Server should be running under a Domain-B service account, otherwise it is very likely that Domain-B will not accept the token from the service and fail.
Thanks for replying to my post.
Actually, Domain A trusts Domain B and Domain B trusts Domain A. Full 2-Way trust.
SQL Server machine was a member of Domain A but now has joined Domain B. Domain A will be going away.
Previous Working Scenario
Agent job runs successfully. Domain A\SQLAgentAcct while logged into Domain A is able to get information about Domain B\Developer. I assume because of the 2-way trust.
Non-working Scenario. Attempting to take Domain A out of the picture.
SQLAgentAcct could not obtain information about Windows NT group/user ‘Domain B\Developer’
Like Syndrake, I was able to log into the server as Domain B\SQLAgentAcct and add Domain B\Developer to local groups. The check names function works great. So, you would think Domain B\SQLAgentAcct would have adequate permissions to query AD.
My AD Admin claims that the Domain B\SQLAgentAcct does not have any restrictions. It is setup like any other user. And, because I am able to query AD outside of SQL, this doesn’t seem to be a AD permissions issue.
What is the service account for SQL Server? The AD query should be running using the AD credentials (if coming from SQL Server Engine).
In my working scenario, the SQL Server service was running as a domain user in Domain A.
In the non-working scenario, the SQL Server service is running as a local account that does not have domain access to Domain B. I set it up this way because I thought it was the SQL Agent account that was actually doing the AD query.
I changed the SQL Server service to run as a domain user account and the agent jobs now appear to be working when a domain account is the owner.
I am going to do some more testing, but I think that the SQL Server service account was my problem.
Thank you very much, Raul.
We have this issue also. I’m going to try maybe setting the trust for delegation rights on the sql svc acct? Could this be a double hop kerberos issue?
Has anyone found any fix for this?
I have the following scenario and solved it this way:
On The SQL Server, error 28005 was constantly logged in the event log:
An exception occurred while enqueueing a message in the target queue.
Error: 15404, State: 19. Could not obtain information about Windows NT group/user ‘ALPHA\myaccount’, error code 0x5.
On the Domain Controller(s) of domain «ALPHA» I could also find event id 4769 and Failure Code 0xc,
which translates to KDC policy rejects request Workstation/logon time restriction.
Log Name: Security
Source: Microsoft-Windows-Security-Auditing
Date: 16.11.2010 07:11:46
Event ID: 4769
Task Category: Kerberos Service Ticket Operations
Level: Information
Keywords: Audit Failure
User: N/A
Computer: DC1.alpha.corp
Description:
A Kerberos service ticket was requested.
Account Information:
Account Name: sqlservice@BETA.CORP
Account Domain: BETA.CORP
Logon GUID:
Service Information:
Service Name: cifs/DC1.alpha.corp
Service ID: S-1-0-0
Solution:
Enable ‘Allowed to authenticate‘ security setting for the service account BETA\sqlservice on the domain controllers computer object in domain ALPHA:
Could not obtain information about Windows NT group user
I am creating a SQL Server Replication using a script. When I try to execute
The job failed. Unable to determine if the owner (STAR\moorer7) of job L3BPT2M-Atlas-14 has server access (reason: Could not obtain information about Windows NT group/user ‘STAR\moorer7’, error code 0x5. [SQLSTATE 42000] (Error 15404)).
This is a job created by a script that defines replication.
How do I debug this?
9 Answers 9
Active Directory is refusing access to your SQL Agent. The Agent should be running under an account that is recognized by STAR domain controller.
We encountered similar errors in a testing environment on a virtual machine. If the machine name changes due to VM cloning from a template, you can get this error.
If the computer name changed from OLD to NEW.
A job uses this stored procedure:
Which uses this one:
Which gives this SQL error 15404
Which I guess is correct, under the circumstances. We added a script to the VM cloning/deployment process that re-creates the SQL login.
In my case I was getting this error trying to use the IS_ROLEMEMBER() function on SQL Server 2008 R2. This function isn’t valid prior to SQL Server 2012.
Instead of this function I ended up using
Significantly more verbose, but it gets the job done.
Just solved this problem. In my case it was domain controller is not accessible, because both dns servers was google dns.
I just add to checklist for this problem:
I was having the same issue, which turned out to be caused by the Domain login that runs the SQL service being locked out in AD. The lockout was caused by an unrelated usage of the service account for another purpose with the wrong password.
The errors received from SQL Agent logs did not mention the service account’s name, just the name of the user (job owner) that couldn’t be authenticated (since it uses the service account to check with AD).
I had to connect to VPN for the publish script to successfully deploy to the DB.
In our case, the Windows service account that SQL Server and SQL Agent were running under were locked out in Active Directory.
I just got this error and it turns out my AD administrator deleted the service account used by EVERY SQL Server instance in the entire company. Thank goodness AD has its own recycle bin.
Ошибка 0x534 при создании схемы данных
Помощь в написании контрольных, курсовых и дипломных работ здесь.
Ошибка при создании схемы данных
Добрый день! Помогите пожалуйста решить проблему! Я создаю базу данных в Access для производства.
Ошибка при создании базы данных
Здравствуйте!Столкнулся с проблемой: при попытке добавить базу данных в решение(правой.
Ошибка при создании базы данных
у меня одна проблема я удалил базу данный по имени ShopDB Сейчас хочу создать опять по такой же.
Ошибка при динамическом создании данных
Приветству.Ррешил я поставить альфа скин в программе, заменил pagecontrol на TsPageControl.
, где [mydbname] – имя базы данных, DOMAIN и user – имя ПК и пользователя соответственно, а ошибка всё равно сохранилась, а владелец не изменился (при том, что SQL запрос прошёл успешно)
Добавлено через 23 минуты
Удалось получить доступ, переименовав имя для входа в «безопасность, имена для входа». Не думал, что это как-то исправит ошибку
Помощь в написании контрольных, курсовых и дипломных работ здесь.
Ошибка при создании Базы Данных
Доброго Времени Суток! Я установил MySQL Server и следующий код по плану должен был создавать файл.
Ошибка при создании базы данных
Создаю базу данных следующей командой: create database имя базы;, но в ответ получаю сообщение об.
Ошибка при создании источника данных
Здравствуйте, помогите пожалуйста. Проблема заключается в следующем: Создал обычное оконное.
Ошибка при создании базы данных
Доброй ночи! Все никак не могу совладать с ошибкой. Есть вспомогательный класс DBHelper public.