как установить pytorch на windows
Установка и настройка PyTorch на компьютере
На предыдущем этапе работы с этим учебником мы обсуждали основы PyTorch и предварительные требования, которые нужно выполнить, чтобы иметь возможность использовать эту библиотеку при создании модели машинного обучения. Выполняя действия этой статьи, мы установим ее на вашем компьютере.
Получение PyTorch
Во-первых, необходимо настроить среду Python.
Мы рекомендуем настроить виртуальную среду Python в Windows, используя в качестве диспетчера пакетов платформу Anaconda. Далее в командах установки предполагается, что вы используете среду Anaconda.
Не забудьте установить Python 3.x. В настоящее время PyTorch в Windows поддерживает только Python 3.x; Python 2.x не поддерживается.
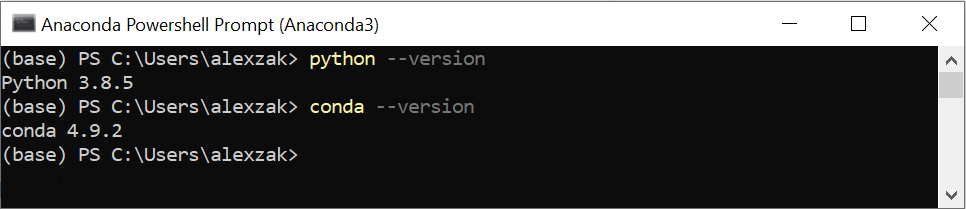
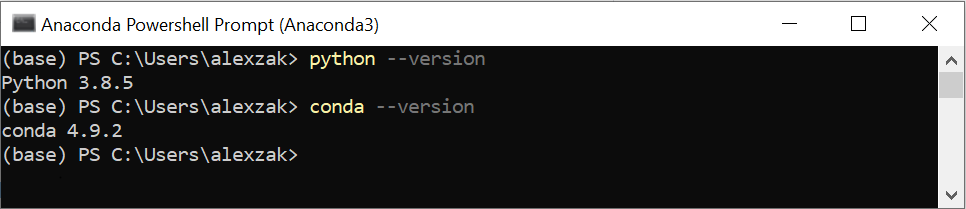
После завершения установки проверьте версии Anaconda и Python.
Проверить версию Python можно с помощью следующей команды: python –-version
Проверить версию Anaconda можно с помощью следующей команды: conda –-version
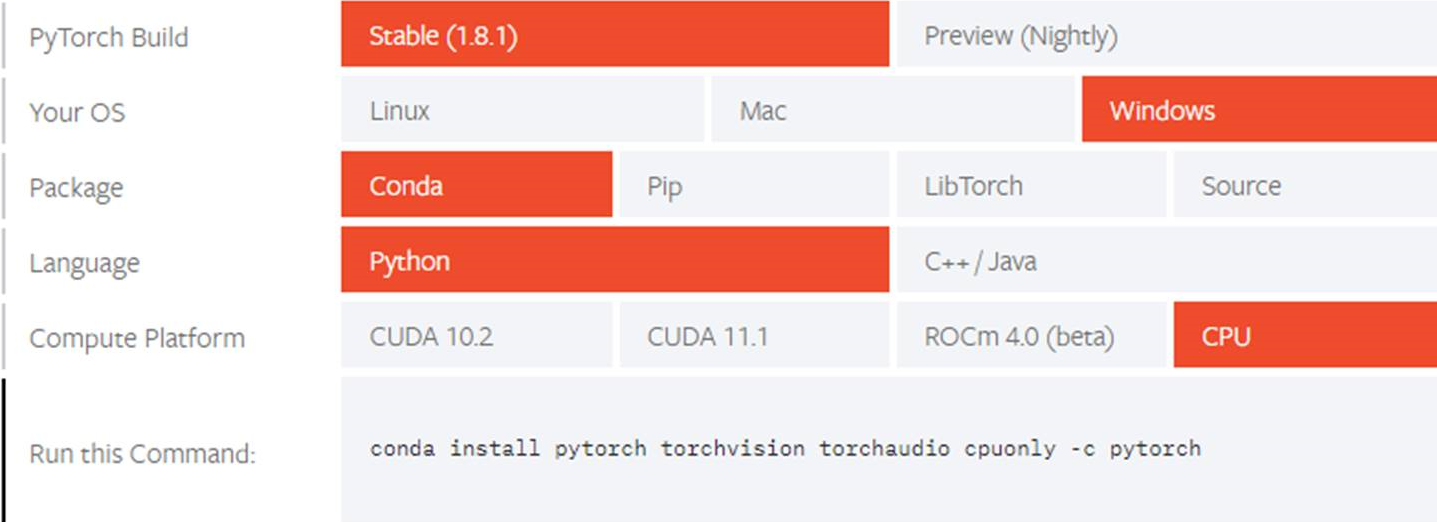
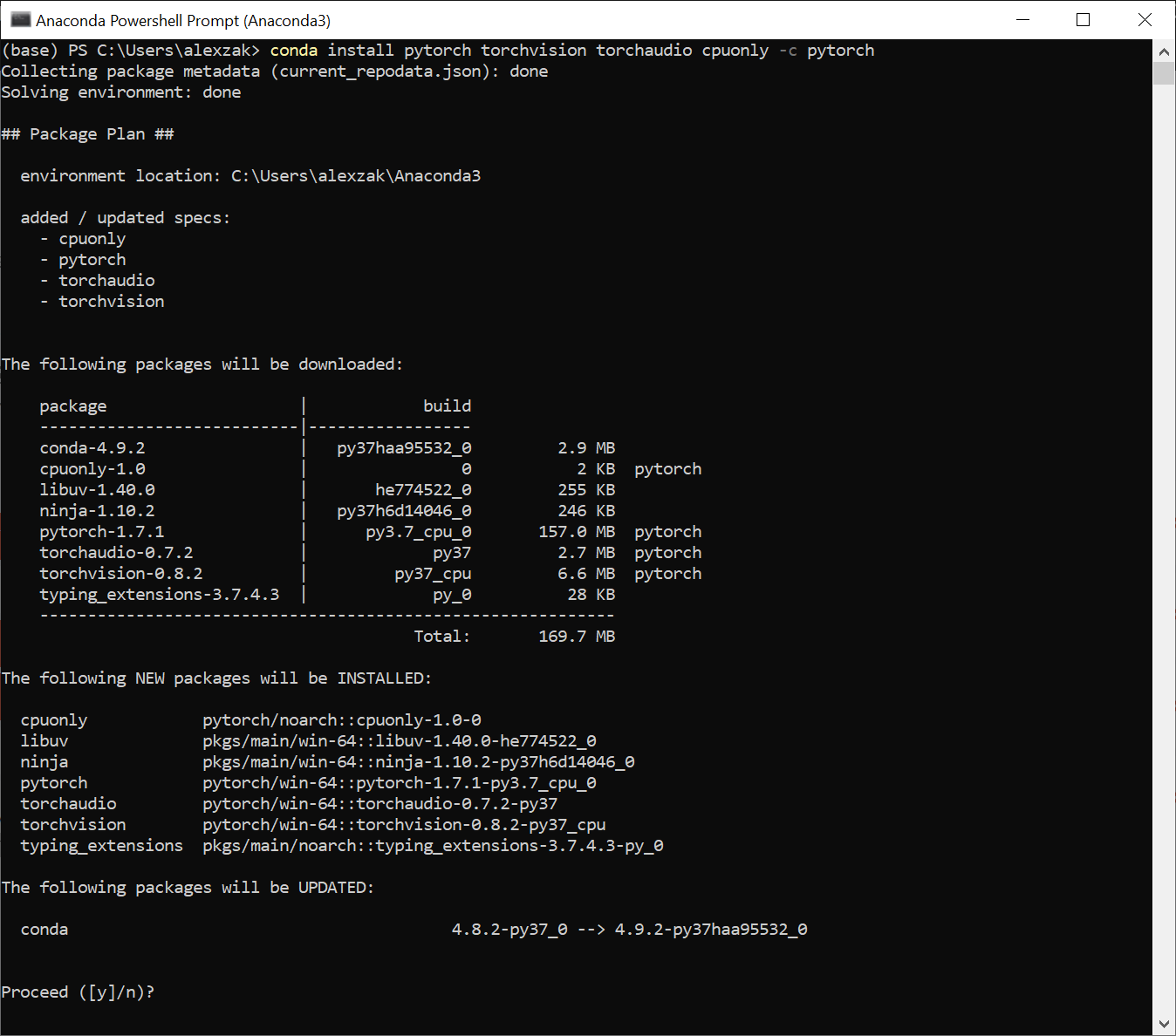
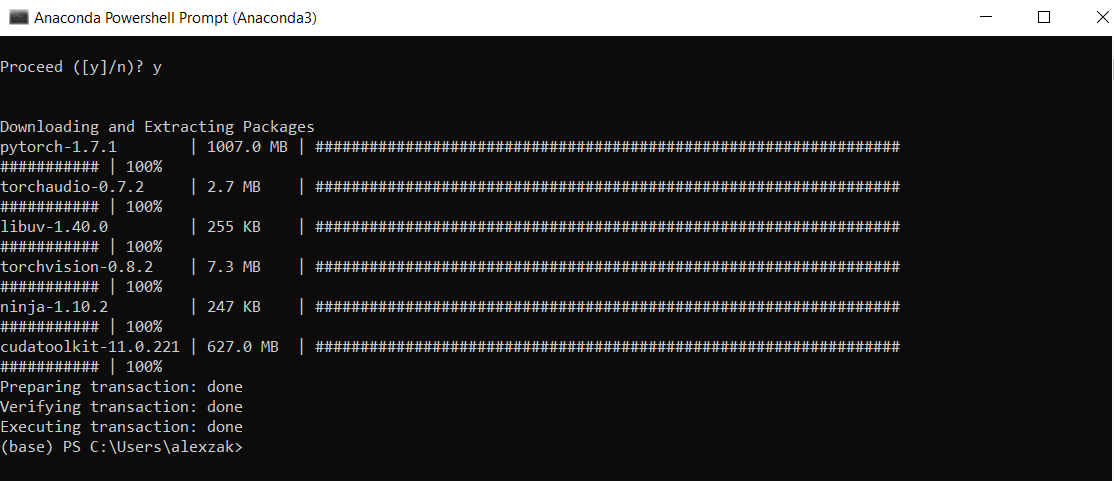
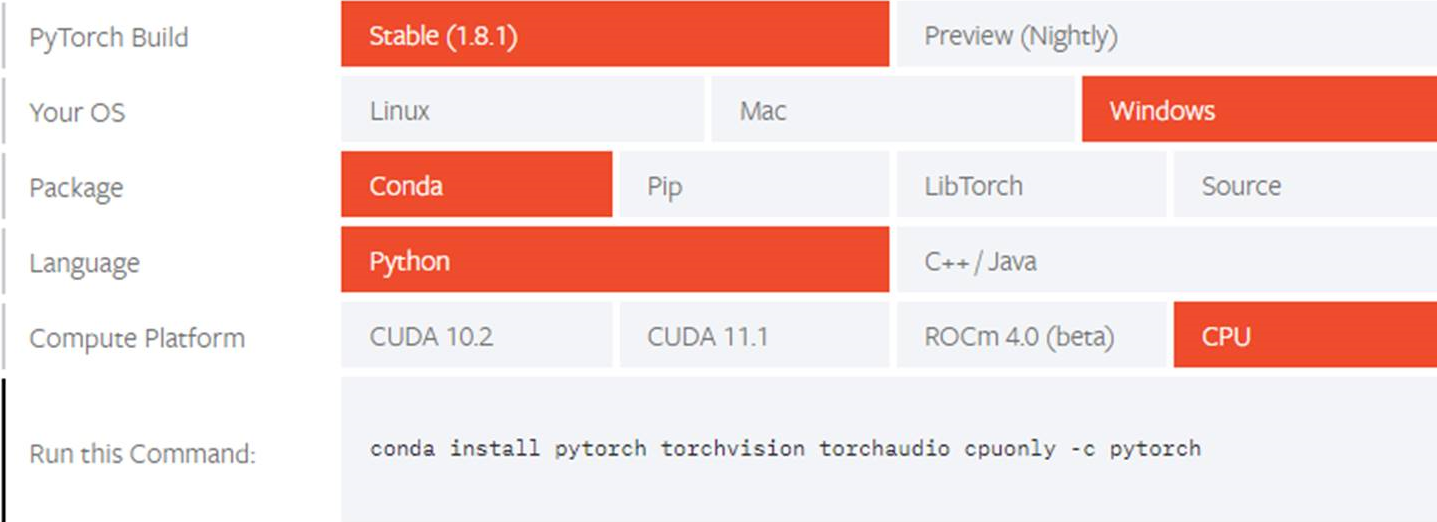
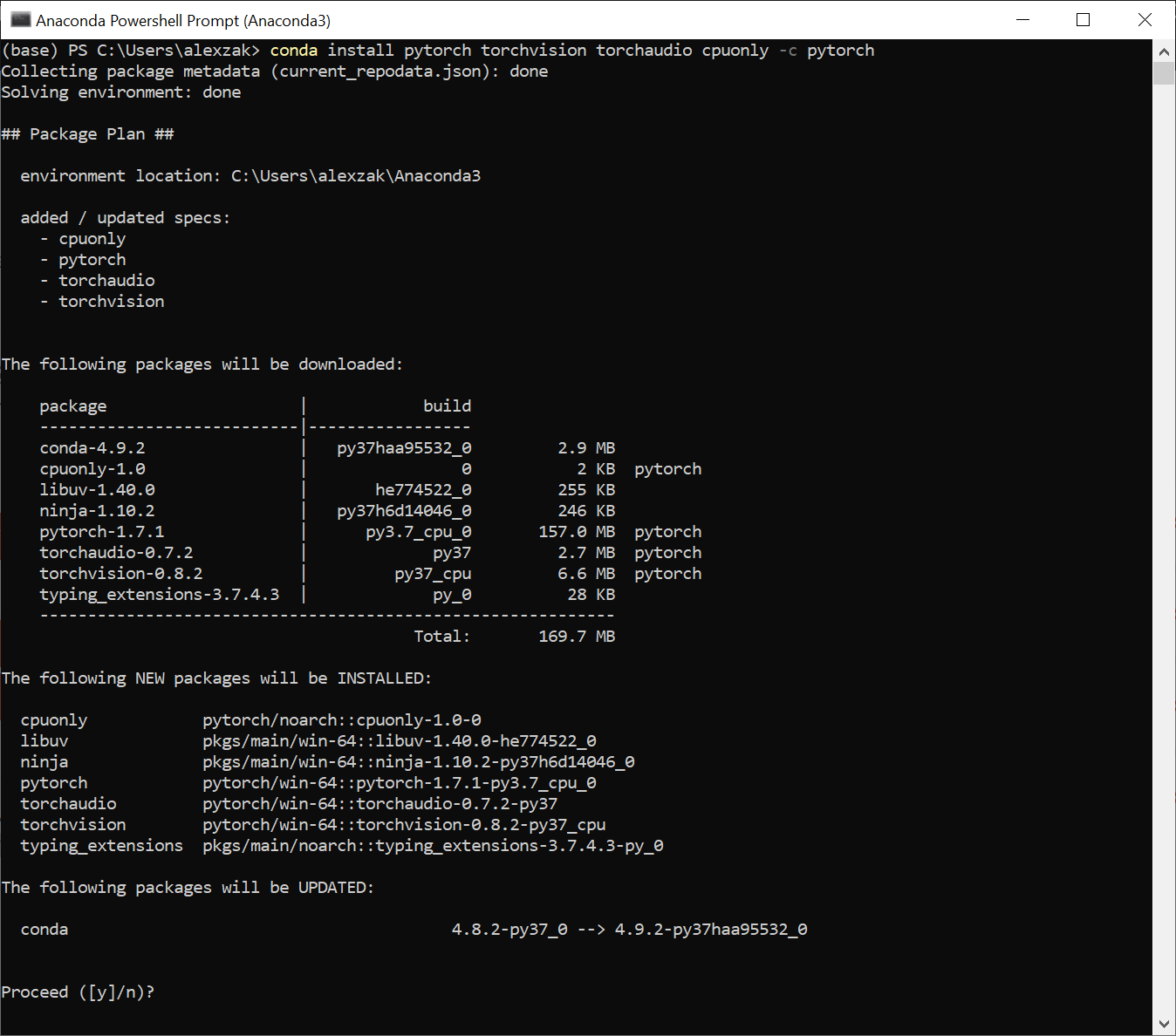
Теперь вы можете установить пакет PyTorch из двоичных файлов с помощью Conda.
Выберите соответствующие сведения об установке PyTorch:
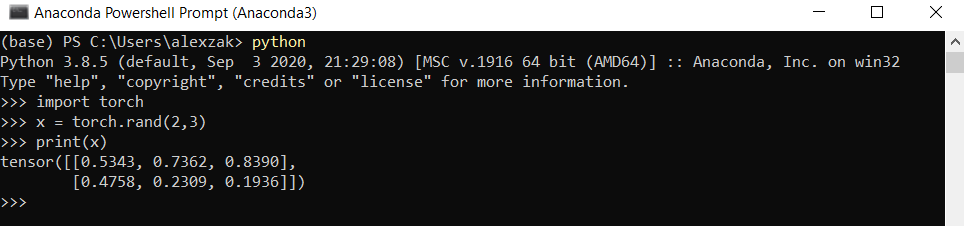
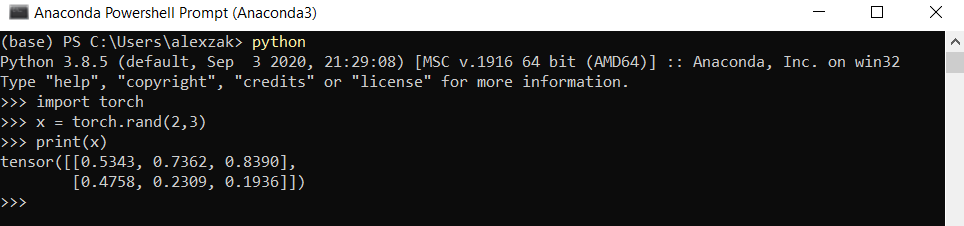
Давайте проверим установку PyTorch, выполнив пример кода PyTorch для создания случайно инициализированного тензора.
Затем введите следующий код:
В качестве вывода должен отображатся случайный тензор 5×3. Числа будут отличаться, однако результат должен выглядеть примерно так, как показано ниже.
Next Steps
Теперь, установив PyTorch, мы можем перейти к настройке данных для нашей модели.
Установка и настройка PyTorch
На предыдущем этапе работы с этим учебником мы обсуждали основы PyTorch и предварительные требования, которые нужно выполнить, чтобы иметь возможность использовать эту библиотеку при создании модели машинного обучения. Выполняя действия этой статьи, мы установим ее на вашем компьютере.
Получение PyTorch
Во-первых, необходимо настроить среду Python.
Мы рекомендуем настроить виртуальную среду Python в Windows, используя в качестве диспетчера пакетов платформу Anaconda. Далее в командах установки предполагается, что вы используете среду Anaconda.
Не забудьте установить Python 3.x. В настоящее время PyTorch в Windows поддерживает только Python 3.x; Python 2.x не поддерживается.
После завершения установки проверьте версии Anaconda и Python.
Проверить версию Python можно с помощью следующей команды: python –-version
Проверить версию Anaconda можно с помощью следующей команды: conda –-version
Теперь вы можете установить пакет PyTorch из двоичных файлов с помощью Conda.
Выберите соответствующие сведения об установке PyTorch:
Давайте проверим установку PyTorch, выполнив пример кода PyTorch для создания случайно инициализированного тензора.
Затем введите следующий код:
В качестве вывода должен отображатся случайный тензор 5×3. Числа будут отличаться, однако результат должен выглядеть примерно так, как показано ниже.
Next Steps
Теперь, установив PyTorch, мы можем перейти к настройке данных для нашей модели.
Install and configure PyTorch on your machine.
In the previous stage of this tutorial, we discussed the basics of PyTorch and the prerequisites of using it to create a machine learning model. Here, we’ll install it on your machine.
Get PyTorch
First, you’ll need to setup a Python environment.
We recommend setting up a virtual Python environment inside Windows, using Anaconda as a package manager. The rest of this setup assumes you use an Anaconda environment.
Be aware to install Python 3.x. Currently, PyTorch on Windows only supports Python 3.x; Python 2.x is not supported.
After the installation is complete, verify your Anaconda and Python versions.
You can check your Python version by running the following command: python –-version
You can check your Anaconda version by running the following command: conda –-version
Now, you can install PyTorch package from binaries via Conda.
Select the relevant PyTorch installation details:
Let’s verify PyTorch installation by running sample PyTorch code to construct a randomly initialized tensor.
Next, enter the following code:
The output should be a random 5×3 tensor. The numbers will be different, but it should look similar to the below.
Interested in learning more? Visit the PyTorch official website
Next Steps
Now that we’ve installed PyTorch, we’re ready to set up the data for our model.
Get Started
Select preferences and run the command to install PyTorch locally, or get started quickly with one of the supported cloud platforms.
Start Locally
Select your preferences and run the install command. Stable represents the most currently tested and supported version of PyTorch. This should be suitable for many users. Preview is available if you want the latest, not fully tested and supported, 1.11 builds that are generated nightly. Please ensure that you have met the prerequisites below (e.g., numpy), depending on your package manager. Anaconda is our recommended package manager since it installs all dependencies. You can also install previous versions of PyTorch. Note that LibTorch is only available for C++.
Additional support or warranty for some PyTorch Stable and LTS binaries are available through the PyTorch Enterprise Support Program.
Installing on macOS
PyTorch can be installed and used on macOS. Depending on your system and compute requirements, your experience with PyTorch on a Mac may vary in terms of processing time. It is recommended, but not required, that your Mac have an NVIDIA GPU in order to harness the full power of PyTorch’s CUDA support.
Currently, CUDA support on macOS is only available by building PyTorch from source
Prerequisites
macOS Version
PyTorch is supported on macOS 10.10 (Yosemite) or above.
Python
It is recommended that you use Python 3.5 or greater, which can be installed either through the Anaconda package manager (see below), Homebrew, or the Python website.
Package Manager
To install the PyTorch binaries, you will need to use one of two supported package managers: Anaconda or pip. Anaconda is the recommended package manager as it will provide you all of the PyTorch dependencies in one, sandboxed install, including Python.
Anaconda
Installation
Anaconda
To install PyTorch via Anaconda, use the following conda command:
To install PyTorch via pip, use one of the following two commands, depending on your Python version:
Verification
To ensure that PyTorch was installed correctly, we can verify the installation by running sample PyTorch code. Here we will construct a randomly initialized tensor.
The output should be something similar to:
Building from source
For the majority of PyTorch users, installing from a pre-built binary via a package manager will provide the best experience. However, there are times when you may want to install the bleeding edge PyTorch code, whether for testing or actual development on the PyTorch core. To install the latest PyTorch code, you will need to build PyTorch from source.
You will also need to build from source if you want CUDA support.
Prerequisites
You can verify the installation as described above.
Installing on Linux
PyTorch can be installed and used on various Linux distributions. Depending on your system and compute requirements, your experience with PyTorch on Linux may vary in terms of processing time. It is recommended, but not required, that your Linux system has an NVIDIA GPU in order to harness the full power of PyTorch’s CUDA support..
Prerequisites
Supported Linux Distributions
PyTorch is supported on Linux distributions that use glibc >= v2.17, which include the following:
Python
Python 3.6 or greater is generally installed by default on any of our supported Linux distributions, which meets our recommendation.
However, if you want to install another version, there are multiple ways:
If you decide to use APT, you can run the following command to install it:
If you use Anaconda to install PyTorch, it will install a sandboxed version of Python that will be used for running PyTorch applications.
Package Manager
To install the PyTorch binaries, you will need to use one of two supported package managers: Anaconda or pip. Anaconda is the recommended package manager as it will provide you all of the PyTorch dependencies in one, sandboxed install, including Python.
Anaconda
You may have to open a new terminal or re-source your
/.bashrc to get access to the conda command.
While Python 3.x is installed by default on Linux, pip is not installed by default.
Installation
Anaconda
No CUDA
To install PyTorch via Anaconda, and do not have a CUDA-capable system or do not require CUDA, in the above selector, choose OS: Linux, Package: Conda and CUDA: None. Then, run the command that is presented to you.
With CUDA
To install PyTorch via Anaconda, and you do have a CUDA-capable system, in the above selector, choose OS: Linux, Package: Conda and the CUDA version suited to your machine. Often, the latest CUDA version is better. Then, run the command that is presented to you.
No CUDA
To install PyTorch via pip, and do not have a CUDA-capable system or do not require CUDA, in the above selector, choose OS: Linux, Package: Pip and CUDA: None. Then, run the command that is presented to you.
With CUDA
To install PyTorch via pip, and do have a CUDA-capable system, in the above selector, choose OS: Linux, Package: Pip and the CUDA version suited to your machine. Often, the latest CUDA version is better. Then, run the command that is presented to you.
Verification
To ensure that PyTorch was installed correctly, we can verify the installation by running sample PyTorch code. Here we will construct a randomly initialized tensor.
The output should be something similar to:
Additionally, to check if your GPU driver and CUDA is enabled and accessible by PyTorch, run the following commands to return whether or not the CUDA driver is enabled:
Building from source
For the majority of PyTorch users, installing from a pre-built binary via a package manager will provide the best experience. However, there are times when you may want to install the bleeding edge PyTorch code, whether for testing or actual development on the PyTorch core. To install the latest PyTorch code, you will need to build PyTorch from source.
Prerequisites
You can verify the installation as described above.
Installing on Windows
PyTorch can be installed and used on various Windows distributions. Depending on your system and compute requirements, your experience with PyTorch on Windows may vary in terms of processing time. It is recommended, but not required, that your Windows system has an NVIDIA GPU in order to harness the full power of PyTorch’s CUDA support.
Prerequisites
Supported Windows Distributions
PyTorch is supported on the following Windows distributions:
The install instructions here will generally apply to all supported Windows distributions. The specific examples shown will be run on a Windows 10 Enterprise machine
Python
Currently, PyTorch on Windows only supports Python 3.x; Python 2.x is not supported.
As it is not installed by default on Windows, there are multiple ways to install Python:
If you use Anaconda to install PyTorch, it will install a sandboxed version of Python that will be used for running PyTorch applications.
If you decide to use Chocolatey, and haven’t installed Chocolatey yet, ensure that you are running your command prompt as an administrator.
For a Chocolatey-based install, run the following command in an administrative command prompt:
Package Manager
To install the PyTorch binaries, you will need to use at least one of two supported package managers: Anaconda and pip. Anaconda is the recommended package manager as it will provide you all of the PyTorch dependencies in one, sandboxed install, including Python and pip.
Anaconda
If you installed Python by any of the recommended ways above, pip will have already been installed for you.
Installation
Anaconda
No CUDA
To install PyTorch via Anaconda, and do not have a CUDA-capable system or do not require CUDA, in the above selector, choose OS: Windows, Package: Conda and CUDA: None. Then, run the command that is presented to you.
With CUDA
To install PyTorch via Anaconda, and you do have a CUDA-capable system, in the above selector, choose OS: Windows, Package: Conda and the CUDA version suited to your machine. Often, the latest CUDA version is better. Then, run the command that is presented to you.
No CUDA
To install PyTorch via pip, and do not have a CUDA-capable system or do not require CUDA, in the above selector, choose OS: Windows, Package: Pip and CUDA: None. Then, run the command that is presented to you.
With CUDA
To install PyTorch via pip, and do have a CUDA-capable system, in the above selector, choose OS: Windows, Package: Pip and the CUDA version suited to your machine. Often, the latest CUDA version is better. Then, run the command that is presented to you.
Verification
To ensure that PyTorch was installed correctly, we can verify the installation by running sample PyTorch code. Here we will construct a randomly initialized tensor.
From the command line, type:
then enter the following code:
The output should be something similar to:
Additionally, to check if your GPU driver and CUDA is enabled and accessible by PyTorch, run the following commands to return whether or not the CUDA driver is enabled:
Building from source
For the majority of PyTorch users, installing from a pre-built binary via a package manager will provide the best experience. However, there are times when you may want to install the bleeding edge PyTorch code, whether for testing or actual development on the PyTorch core. To install the latest PyTorch code, you will need to build PyTorch from source.
Prerequisites
You can verify the installation as described above.
Windows FAQ¶
Building from source¶
Include optional components¶
There are two supported components for Windows PyTorch: MKL and MAGMA. Here are the steps to build with them.
Speeding CUDA build for Windows¶
Visual Studio doesn’t support parallel custom task currently. As an alternative, we can use Ninja to parallelize CUDA build tasks. It can be used by typing only a few lines of code.
One key install script¶
You can take a look at this set of scripts. It will lead the way for you.
Extension¶
CFFI Extension¶
The support for CFFI Extension is very experimental. There’re generally two steps to enable it under Windows.
First, specify additional libraries in Extension object to make it build on Windows.
Second, here is a workground for “unresolved external symbol state caused by extern THCState *state; ”
Change the source code from C to C++. An example is listed below.
Cpp Extension¶
This type of extension has better support compared with the previous one. However, it still needs some manual configuration. First, you should open the x86_x64 Cross Tools Command Prompt for VS 2017. And then, you can start your compiling process.
Installation¶
Package not found in win-32 channel.¶
PyTorch doesn’t work on 32-bit system. Please use Windows and Python 64-bit version.
Import error¶
The problem is caused by the missing of the essential files. Actually, we include almost all the essential files that PyTorch need for the conda package except VC2017 redistributable and some mkl libraries. You can resolve this by typing the following command.
As for the wheels package, since we didn’t pack some libraries and VS2017 redistributable files in, please make sure you install them manually. The VS 2017 redistributable installer can be downloaded. And you should also pay attention to your installation of Numpy. Make sure it uses MKL instead of OpenBLAS. You may type in the following command.
Another possible cause may be you are using GPU version without NVIDIA graphics cards. Please replace your GPU package with the CPU one.
This is actually an upstream issue of Anaconda. When you initialize your environment with conda-forge channel, this issue will emerge. You may fix the intel-openmp libraries through this command.
Usage (multiprocessing)¶
Multiprocessing error without if-clause protection¶
Multiprocessing error “Broken pipe”¶
This issue happens when the child process ends before the parent process finishes sending data. There may be something wrong with your code. You can debug your code by reducing the num_worker of DataLoader to zero and see if the issue persists.
Multiprocessing error “driver shut down”¶
Please update your graphics driver. If this persists, this may be that your graphics card is too old or the calculation is too heavy for your card. Please update the TDR settings according to this post.
CUDA IPC operations¶
They are not supported on Windows. Something like doing multiprocessing on CUDA tensors cannot succeed, there are two alternatives for this.
2. Share CPU tensors instead. Make sure your custom DataSet returns CPU tensors.