логи dns сервера windows
Аудит DNS запросов клиентов в Windows Server, логи DNS
В этой статье мы рассмотрим, как включить логирование всех DNS запросов пользователей, которые получает DNS сервер на Windows Server, и выполнить их анализ. У меня такая возникла, когда понадобилось декомисснуть старый контроллер домена Active Directory в филиале и нужно было понять, какие устройства все еще используют этот DNS сервер. После включения DNS лога и его анализа я смог найти оставшиеся устройства и перенастроить их на другие DNS сервера. Также эта методика поможет вам найти в сети хосты с подозрительной активность (обращения к вредоносным URL, хостам управления ботнетами и т.д.).
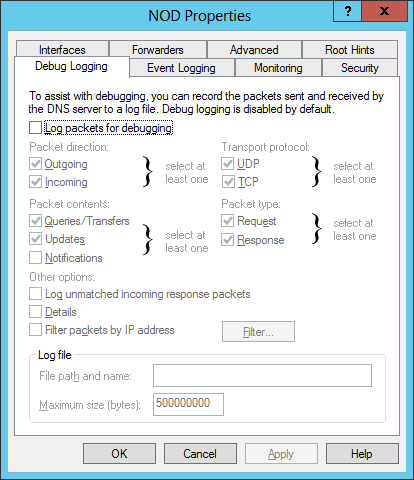
По умолчанию в Windows Server отключено логирование DNS всех пакетов. Чтобы его включить:
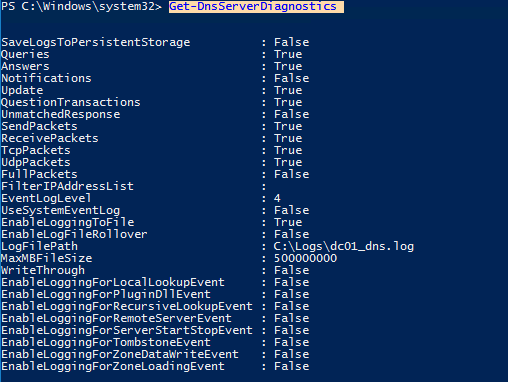
Также вы можете включить логирование DNS или получить текущие настройки с помощью PowerShell:
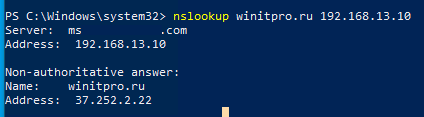
Теперь выполните с любого компьютера DNS запрос к этому серверу (IP адрес нашего DNS хоста с Windows Server 192.168.13.10), например:
nslookup winitpro.ru 192.168.13.10
Данный запрос вернул клиенту IP адрес запрошенного сервера.
Проверим теперь, что этот запрос отобразился в логе DNS сервера.
Для этого, выполним поиск в текстовом логе по IP адресу клиента (192.168.13.200). Можно открыть лог файл в блокноте, а можно выполнить поиск по нему с помощью PowerShell:
Событие выглядит так:
Как вы видите, в логе указано: от клиента 192.168.13.200 получен (rcv) DNS запрос по протоколу UDP на разрешение имени (8)winitpro(2)ru(0), а затем DNS сервер успешно (NOERROR) отправил ему ответ (snd).
Из-за специфического формата, анализировать DNS лог вручную довольно сложно, поэтому для преобразования DNS запросов в более удобный формат можно использовать готовый PowerShell скрипт Get-DNSDebugLog.ps1.
Скачайте данный файл к себе на диск. Затем разрешите запуск PowerShell скриптов в текущей консоли:
Импортируйте функцию из файла Get-DNSDebugLog.ps1 в свою сессию:
Теперь можно преобразовать DNS лог в более удобный вид:
[Или можно экспортировать полученный результат в CSV файл для дальнейшего анализа в Excel (либо можно напрямую обращаться из PowerShell к Excel файлу и заносить в него нужные строки).
Вы можете экспортировать данный файл в Excel и использовать его для анализа DNS запросов (в файле есть адреса хостов и DNS имена, за которыми они обращались к вашему DNS серверу).
Также для анализа лог файла с DNS запросами можно использовать Log Parser 2.2 (https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/archive/blogs/secadv/parsing-dns-server-log-to-track-active-clients). Например, следующая команда выведет информацию о количестве DNS запросов с каждого IP адреса:
В этом примере мы использовали текстовые файлы для сбора DNS логов. В Windows Server 2012+ вы можете записывать DNS запросы прямо в журнал Event Viewer ( Microsoft-Windows-DNS-Server/Audit ). Но на мой взгляд текстовые DNS логи анализировать гораздо проще.
После включения DNS лога и его анализа я нашел IP адреса устройств, которые все еще используют этот DNS сервер и перенастроил их на другие DNS сервера. Теперь, если старый DC не содержит FSMO ролей, то его можно спокойно удалять (события логона пользователей при этом роли не играют).
DNS Logging and Diagnostics
Applies To: Windows Server 2012 R2
Enhanced DNS logging and diagnostics is available by default in Windows ServerВ® 2016 Technical Preview. This feature is also available in Windows ServerВ® 2012 R2 when you install the query logging and change auditing hotfix, available from https://support.microsoft.com/kb/2956577.
DNS logging and diagnostics
See the following sections in this topic:
Performance considerations
DNS server performance can be affected when additional logging is enabled, however the enhanced DNS logging and diagnostics feature in Windows Server 2012 R2 and Windows Server 2016 Technical Preview is designed to have a very low impact on performance. The following sections discuss DNS server performance considerations when additional logging is enabled.
Debug logging
Prior to the introduction of DNS analytic logs, DNS debug logging was an available method to monitor DNS transactions. DNS debug logging is not the same as the enhanced DNS logging and diagnostics feature discussed in this topic. Debug logging is discussed here because it is also a tool that is available for DNS logging and diagnostics. See Using server debugging logging options for more information about DNS debug logging. The DNS debug log provides extremely detailed data about all DNS information that is sent and received by the DNS server, similar to the data that can be gathered using packet capture tools such as network monitor. Debug logging can affect overall server performance and also consumes disk space, therefore it is recommended to enable debug logging only temporarily when detailed DNS transaction information is needed.
Audit and analytic event logging
Enhanced DNS logging and diagnostics in Windows Server 2012 R2 and later includes DNS Audit events and DNS Analytic events. DNS audit logs are enabled by default, and do not significantly affect DNS server performance. DNS analytical logs are not enabled by default, and typically will only affect DNS server performance at very high DNS query rates. For example, a DNS server running on modern hardware that is receiving 100,000 queries per second (QPS) can experience a performance degradation of 5% when analytic logs are enabled. There is no apparent performance impact for query rates of 50,000 QPS and lower. However, it is always advisable to monitor DNS server performance whenever additional logging is enabled.
Installing and enabling DNS diagnostic logging
Perform the following procedures to install and enable DNS diagnostic logging on Windows Server 2012 R2. To install DNS diagnostic logging, the computer must be running the DNS Server role service.
If the DNS server is running Windows Server 2016 Technical Preview or later, diagnostic logging is already installed and you can skip the first procedure, performing only the steps in To enable DNS diagnostic logging below.
Membership in the Administrators group, or equivalent, is the minimum required to complete these procedures. Review details about using the appropriate accounts and group memberships at Local and Domain Default Groups (https://go.microsoft.com/fwlink/?LinkId=83477).
To install DNS diagnostic logging
If the DNS server is running Windows Server 2012 R2, download the hotfix from https://support.microsoft.com/kb/2956577.
Double-click the self-extracting file, for example 475151_intl_x64_zip.exe.
In the Microsoft Self-Extractor dialog box, click Continue.
Type a location where you want to save the extracted files, for example C:\hotfix. If the directory does not yet exist, you will be asked if you wish to create it. Click Yes and confirm that All files were successfully unzipped is displayed, then click Ok.
In the location where files were unzipped, double-click the Windows Update file, for example Windows8.1-KB2956577-v2-x64.msu.
The Windows Update Standalone Installer will verify that the computer meets requirements to install the update. These requirements include some prerequisite updates. When verification is complete, click Yes when asked if you wish to install the Hotfix for Windows (KB2956577).
If recently downloaded updates have not yet been installed, you might need to restart the computer before the current hotfix can be installed. If this is required, you must restart the computer first and then run the Windows8.1-KB2956577-v2-x64.msu a second time after the computer has completed installing necessary updates. The Windows Update Standalone Installer will notify you that installation of the hotfix is not yet complete. If this happens, and you are prompted to restart the computer, click Restart Now.
If the computer is ready to install the update when you run the hotfix, installation will complete and you must restart the computer for the update to take effect. If Installation complete is displayed, click Restart Now for the update to take effect.
You can confirm that the hotfix was successfully installed by viewing installed updates in the Programs and Features control panel. If the update is successfully installed, Hotfix for Microsoft Windows (KB2956577) will be displayed. You can also verify installation of the hotfix by typing wmic qfe | find «KB2956577» at an elevated command prompt. The URL and date of installation for the hotfix will be displayed if it was successfully installed.
To enable DNS diagnostic logging
Type eventvwr.msc at an elevated command prompt and press ENTER to open Event Viewer.
In Event Viewer, navigate to Applications and Services Logs\Microsoft\Windows\DNS-Server.
Right-click DNS-Server, point to View, and then click Show Analytic and Debug Logs. The Analytical log will be displayed.
Right-click Analytical and then click Properties.
Under When maximum event log size is reached, choose Do not overwrite events (Clear logs manually), select the Enable logging checkbox, and click OK when you are asked if you want to enable this log. See the following example.
Click OK again to enable the DNS Server Analytic event log.
By default, analytic logs are written to the file: %SystemRoot%\System32\Winevt\Logs\Microsoft-Windows-DNSServer%4Analytical.etl.
See the following sections for details about events that are displayed in the DNS server audit and analytic event logs.
Using DNS server audit and analytic events
DNS logs are compatible with Event Tracing for Windows (ETW) consumer applications such as logman, tracelog, and message analyzer. For more information about using event tracing, see About Event Tracing.
Using ETW consumers
You can use ETW consumers such as tracelog.exe with DNS server audit and analytic events by specifying a GUID of .
You can get tracelog.exe by downloading and installing the Windows Driver Kit (WDK). Tracelog.exe is included when you install the WDK, Visual Studio, and the Windows SDK for desktop apps. For information about downloading the kits, see Windows Hardware Downloads. For example, when you download and install Windows Driver Kit (WDK) 8 and accept the default installation path, tracelog.exe is available at C:\Program Files (x86)\Windows Kits\8.0\Tools\x64\tracelog.exe.
For more information about using tracelog.exe, see Tracelog Command Syntax. The following examples demonstrate how to use tracelog.exe with DNS audit and analytic event logs:
The following command will enable both analytical and audit logging:
While the trace is active, all analytical and audit events will be recorded in the C:\analytic_audit.etl file that was specified on the command line. You can stop tracing by issuing a stop command:
The following example enables just the analytical channel and matches only the keywords to 0x7FFFF:
A logging level of 5 is used in the previous examples. The following logging levels are available:
Only critical events are logged, for example process exit or termination. If no logging level is given by the user this level is used by default.
Only severe error events are logged, for example failures to complete a required task.
Errors that can cause a service issue, but are acceptable or recoverable, for example the first attempt to contact a forwarder has failed.
Very high-level events are recorded in the event log. These might include one message for each major task performed by the service. Use this setting to begin an investigation when the location of the problem is in doubt, for example a scavenger thread was started.
All events are logged. This provides a complete log of the operation of the service. Use this level when the problem is traced to a particular category or a small set of categories.
Audit events
DNS server audit events enable change tracking on the DNS server. An audit event is logged each time server, zone, or resource record settings are changed. This includes operational events such as dynamic updates, zone transfers, and DNSSEC zone signing and unsigning. The following table summarizes DNS server audit events.
Table 1: DNS Server Audit Events
Логи dns сервера windows
To turn on DNS logging for a Microsoft Windows Server 2012 system which is functioning as a DNS server, take the following steps:
If you wish to delete an existing log file that is in use and start a new one, right-click on the DNS server in the DNS Manager window, select All Tasks, then Stop. You can then move or delete the log file, right-click on the DNS server again, select All Tasks, then Start to restart logging.
When you check the log file, entries will appear such as the following:
The entries above show the system with IP address 192.168.0.42 queried the DNS server for the address of imap-mail.outlook.com. The Windows Server 2012 DNS server did not know the IP address, so it in turn queried a DNS forwarder system at 10.255.176.137. It received a response from the DNS forwarder and returned the response to the system at 192.168.0.42. The numbers you see for (9)imap-mail(7)outlook(3)com(0) reflect the number of characters in various parts of the address. E.g., imap-mail is 9 characters, outlook is 7 characters, and com is 3 characters.
A valuable and free tool which can aid you in examining Microsoft Windows DNS log files is Windows DNS Log Analyser.
If you wish to rotate the log file daily, you can use the instructions at Rotate the DNS server log file on a Windows server, though, since the at command is deprecated, you will need to use the schtasks command, instead of the at command. A command similar to the one shown below can be used to run the batch file at one minute after midnight every night:
I can check on the status of the avove scheduled task as shown below:
In the above example, the task was submitted on February 19, 2015.
Be sure to read Part 1 and Part 3 of our DNS Log Collection series, in case you missed them.
DNS Log Collection on Windows
If you need to reduce the cost of DNS security and increase efficiency through centralizing DNS log collection, where would you start? Answering this question requires knowledge and awareness of the challenges and opportunities available on the Windows platform. While Windows DNS server is a common technology serving many types of organizations, from local domains to large multi-site enterprises, the possibilities are not necessarily that well-known within the context of comprehensive, site-wide log collection. This article distills the main concepts essential to planning and deploying such an implementation into this article, which serves as the second part of the DNS log collection series. To start, this article will touch on log sources that are generated by Windows DNS servers as well as the DNS requests of the clients they serve.
Windows DNS Log Sources
You may know that there are numerous ways of collecting DNS logs within the Windows environment:
Collecting DNS query logs via Sysmon
Collecting traces directly with Event Tracing for Windows (ETW) DNS Providers
Collecting from the relevant Windows Event Log channels
The deployment and resources to be used for DNS log collection will also depend on whether the logs will be collected from the DNS server (a critical asset) or from DNS clients. Each of these will be covered in further detail in this blog post.
Collecting DNS Query Logs from Sysmon
As of Sysmon version 10.0, there is a DNS Query logging feature to collect DNS query logs from clients. These events are generated when a process executes a DNS query, whether the result is successful or fails, cached or not.
Depending on how Sysmon is configured, you can also set additional rules in the configuration file for Sysmon in relation to Event ID 22: DNSEvent (DNS query). This is advisable due to the noisy nature of this type of event. These types of additions can be:
Exclusion rules to avoid logging reverse DNS lookups
Exclusion rules about which domains to exclude. If excluding certain top level domains (to reduce the amount of logs collected), be more specific with domains
Rules to exclude IPv6 lookups
Rules to omit domains typically used in sandboxes like localhost
Rules to omit queries involving popular third-party applications like Google, Mozilla, as well as CDNs
Rules to omit sites that involve social media widgets like Disqus
Rules to exclude ad serving sites and other ad-related services These are only suggestions for rules and are by all means non-exhaustive. There are Sysmon configuration samples available online for use and adaptation.
Since DNS queries generate a large amount of logs, you may opt to forward Sysmon DNS events in their own output stream to a central log server instead of merging them with other DNS client event sources.
Collecting from DNS ETW Providers
The DNS ETW providers with their corresponding GUIDs are displayed in the table below.
DNS Server Trace Provider
Most of the time, ETW is not considered as a log source, either because it is not widely known, or because special tools are needed to keep track of log traces (see Solving Windows Log Collection Challenges with Event Tracing). In addition, these tools can negatively affect DNS server performance, especially if they are set to continuously collect and write event traces to disk or convert to a format like JSON before being forwarded to a remote host.
Enhanced Windows DNS Event Log Logging
Enhanced DNS Server audit events are available via both the Windows Event Log channels, such as the Microsoft-Windows-DNSServer/Audit channel, as well as directly from the Windows Event Tracing (ETW) provider. These enable change tracking on Windows DNS Server, provided audit events are set to be logged in the Group Policy Editor. If enabled, an audit event is logged for each instance when changes are made to the DNS server such as:
Windows DNS Audit Events
Zone operations – zone deletions, updates, zone record creation and deletion, zone scope creation and deletion, online signing (zone signing/ unsigning/resigning), pausing/reloading/resuming zones
DNSSEC operations – key rollover events, export/importing of DNSSEC metadata, addition of trust point
Cache operations (cache purge events)
Policy operation events – creation/deletion/updating of records such as client subnet records, server level policies or zone level policies
Other server operations – restarting the server, clearing of debug logs, clearing of statistics, scavenging operations
These audit events represent important operations for any DNS server. They can provide very useful information for security and compliance reasons, as well as for incident response.
Ensure that auditing is enabled on Windows DNS Server via the Group Policy Management Editor. You can also configure auditing on the target object via the ADSIEDIT.MSC console by making the necessary changes for the auditing properties of that object.
Windows DNS Analytical Events
DNS analytical events differ from DNS auditing in that they are generated each time Windows DNS Server processes a request. They need to be enabled on the DNS server before logging can happen.
Types of DNS Analytical events include:
Look up events – response success/failure, CNAME lookups, internal lookups
Recursive query events
Dynamic update events
Active Directory and Native DNS Auditing
DNS is automatically installed with Active Directory as the Global Catalog server for the forest and domain. There are a number of features available in Windows DNS Server, such as Native DNS Auditing.
However, systems prior to 2012 R2, or 2012 R2 without hotfix 2956577 do not have native DNS auditing capabilities included. When this is enabled, DNS changes can be audited by enabling AD Directory Services auditing. For more information, see the AD DS Auditing Step-by-Step Guide on Microsoft Docs.
Collecting File-based Microsoft DNS Debug Log Files
The DNS debug file is important since it contains detailed information on DNS queries and activity that is sent and received by the DNS server.
The following debug log sample displays a simple DNS query test from Windows DNS Server:
Due to the amount of logs being generated from DNS debug logging, it is recommended to rotate logs and have them collected on a central server. Also, parsing the logs is suggested, in order to select which logs to enrich. Although DNS debug logging has some advantages, it does come with some additional caveats worth considering:
Due to the way Microsoft handles log rollover of DNS debug logs, if the log file is located on any drive other than the C: drive, the Windows DNS service may not recreate the debug log file after a rollover. See The disappearing Windows DNS debug log for an in-depth analysis of this issue.
The log information gleaned from DNS debug logging is inherently unstructured. Parsing is required to create usable event logs. If the Details option has been selected, regular expressions are needed to parse the event fields. Such configurations are complex and can be associated with additional performance overhead. For busy DNS servers, this would not be a recommended option. For more information see File-based DNS Debug Logging.
Performance Considerations
Depending on which of these logging methods you use, there are a few variables that can affect performance:
The DNS server’s hardware specifications.
The QPS (queries per second) rate.
The place where log enrichment or parsing is done. It can be done either locally or on a central logging server after the logs are received.
The type of logging taking place. It is recommended to enable DNS debug logging only temporarily as needed.
All these factors play a role in influencing log performance.
What can NXLog do?
NXLog simplifies DNS log collection by providing a single software solution that incorporates the various technologies required to efficiently collect DNS related logs. NXLog offers the following methods for the above discussed DNS logging technologies.
Use the im_msvistalog module and add the relevant Query in the configuration file. Find out more at Collecting DNS logs via Sysmon in the NXLog User Guide.
ETW (Event Tracing for Windows) Collection
There is a module, im_etw, that is specifically designed to collect logs from ETW providers without much performance overhead. It acts both as a Controller and a Consumer (see Using NXLog as a Single Agent Solution to Collect ETW Logs).
Native Windows Event Log Collection
For DNS events that can be collected from the Windows Event Log, including Sysmon, use the im_msvistalog module and specify a query for the name of the channel and channel type. You can also add additional filtering to the query. See Windows Event Log.
File-based Log Collection from the Windows DNS Debug File
There is a section in our User Guide detailing the steps involved for the setup of DNS debug logging including Parsing Non-Detailed Logs With xm_msdns.
Conclusion
With this article, you have learned about the opportunities and challenges with these modes of Windows DNS log collection: Sysmon, Event Tracing for Windows (ETW), Windows Event Log and Windows DNS debug file logging. You have also learned about possible DNS performance considerations and the solutions available for DNS log collection. With this knowledge of the various solutions available, you can avoid the pitfalls of deploying less efficient solutions, or ending up with a deployment that is either logging too many or not enough DNS events.
DNS, for many reasons, is an important asset that must not be overlooked. It is known that attackers are abusing DNS, and it is through efficient and reliable DNS log collection that you can reap the benefits of this essential component of security monitoring. Our white paper, The Importance of DNS Logging in Enterprise Security expands on this theme.
NXLog Ltd. develops multi-platform log collection tools that support many different log sources, formats, transports, and integrations. The tools help administrators collect, parse, and forward logs so they can more easily respond to security issues, investigate operational problems, and analyze event data. NXLog distributes the free and open source NXLog Community Edition and offers additional features and support with the NXLog Enterprise Edition.
This document is provided for informational purposes only and is subject to change without notice. Trademarks are the properties of their respective owners.


.jpeg)
.jpeg)